Babies With Spina Bifida: Causes And Treatments
Spina bifida is a congenital malformation of the spinal column of the fetus. It develops during gestation, when the spinal column that is still forming does not close properly around the spinal cord and nerves, leaving an opening that exposes them. Today we are talking about newborns with spina bifida.
Symptoms of spina bifida
Being a spinal malformation, spina bifida can cause physical and brain disabilities. The severity of symptoms varies, as there are different types of spina bifida. It will mainly depend on:
- The size of the opening.
- From the point of the spinal column affected. The higher the malformation is, the greater the consequences.
- Whether the nerves and spinal cord are involved or not.
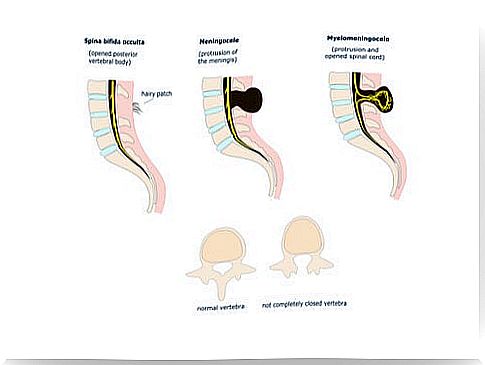
According to these criteria, two types of spina bifida are classified: open spina bifida, which is subdivided into myelomeningocele and meningocele , and spina bifida occulta.
Meningocele
Meningocele affects the meningeal membrane, which is the membrane that covers and protects the brain and spinal cord. Coming out of the opening formed in the spinal column, a fluid-filled sac (meningocele) is created.
Children with this condition can suffer from various health problems based on damage to the nerves surrounding the spine. For example, they may have muscle paralysis to varying degrees or have learning problems, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is the most common form of spina bifida. It is the most severe form of this malformation and causes disabilities ranging from moderate to severe, even causing loss of mobility or sensation in the legs.
It occurs when the meningeal membrane and the lower end of the spinal cord protrude from the opening in the spine and form a fluid-filled sac. This pouch that protrudes over the back of the fetus can burst during delivery leaving the marrow and nerves exposed.
In addition to bone or muscle problems, newborns with myelomeningocele spina bifida usually also suffer from hydrocephalus, a buildup of fluid in or around the brain.
Spina bifida occulta
It is the mildest form of spina bifida and can even go unnoticed. Its name indicates that in this case the malformation is “hidden” under the skin.
Even if hidden, the skin corresponding to the area of the opening may have a birthmark or dimple. Inside, the spinal cord can be “attached” to the tissue, rather than being free, so the nerves are not affected.
Most babies with spina bifida occulta have no long-term problems. Indeed, many times it is diagnosed in late childhood or even in adulthood.
What are the causes of spina bifida?
Not all causes of spina bifida are known yet. It is necessary to investigate the factors that intervene in the development of this malformation, such as genetics or the environment. However, it is known for certain that it is related to low folic acid levels.
Spina bifida forms during the first few weeks of pregnancy, often even before the mother-to-be finds out she is pregnant. Taking folic acid during gestation (400 micrograms per day) helps reduce the risk of malformation. However, it does not guarantee a healthy pregnancy.
Additional advice that the mother can follow to prevent this malformation are:
- Consult your doctor about the best treatment to follow. Just as no two people are alike, no two pregnancies are identical. It is best to follow a personalized treatment that meets all the needs of mother and child.
- Inform yourself appropriately about the components of the medications, vitamins and supplements you are taking. During pregnancy, the body reacts differently to some medicines.
- Check your body temperature. A high fever can increase the chances of the fetus developing spina bifida.
Infants with spina bifida: treatment
Treatment for newborns with spina bifida varies according to the severity of the malformation. Depending on the compromised systems, over time the child will need the intervention of different specialists. These include not only doctors, but also therapists, social workers and associations who offer their support and understanding.
In infants with spina bifida occulta, no treatment may be needed. If the spinal cord is “attached”, surgery will be required to separate it from the tissue. After the operation, babies usually do not have any problems, but the marrow may “stick” again.
Children with meningocele, on the other hand, must be operated on during the first months of life. With surgery, the meningeal membrane is repositioned inside the body and the opening is closed.
In the case of myelomeningocele spina bifida, the process is similar: the baby needs to be operated on, but between the first and second day after birth. If the malformation is diagnosed during the early stages of pregnancy, it is possible to operate at the 25th week to correct it. It will also be necessary to intervene on hydrocephalus if the child suffers from it.