How To Identify Appendicitis In Children?
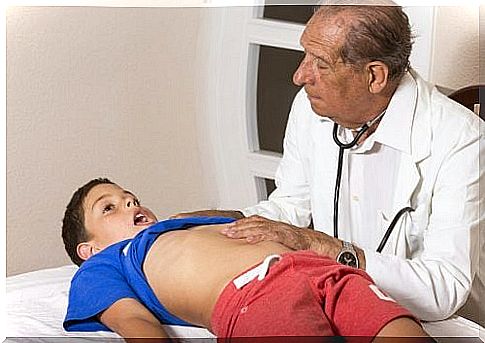
The classic symptoms experienced by adults are not reliable in identifying appendicitis in children. In fact, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting are not exclusive indicators of this pathology.
It is not easy to diagnose this disease in children, which, in fact, can put a strain on the skills of the pediatrician. Symptoms of appendicitis in children are similar to those of other diseases, such as gastroenteritis, food poisoning or respiratory disorders.
Only 33% of pediatric cases have the symptoms described in the medical literature. Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to the occurrence of certain warning signs.
What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix and usually occurs because the appendix becomes blocked. It can be caused by hardened stools, an infection, or inflammation of the lymph nodes in the intestine.
If the appendix ruptures, we are faced with a serious disease. When this happens, bacteria are released in the abdominal cavity, which can cause a severe infection.
Appendicitis usually affects male adolescents and young people in their 20s. In children between one and four years of age, the average annual incidence is between 1 and 2 cases in 10,000 children.
Cases have also been found among newborns, from 0 to 30 days old. These are episodes at risk of death. In 80% of these cases, the diagnosis is made by autopsy.

Because of the difficulty in directly associating the symptoms of appendicitis with this disease, medical assistance is of paramount importance. Between 20% and 30% of reported cases from pediatric studies have appendix rupture.
For physiological reasons, the spread of infection after rupture is imminent. For this reason, peritonitis is considered a serious disease, which, in some cases, can be fatal.
Identifying appendicitis in children
In fact, appendicitis is not very common in children. This is the main reason why its symptoms are often confused with those of other diseases. It will therefore be necessary to pay particular attention to abdominal pain, which is one of the most obvious signs.
The pain caused by appendicitis begins in the navel region and, over a few hours, extends to the lower and right side of the abdomen. The first thing to do is to determine the severity of the pain. If the child is in pain but continues to play, eat, and laugh, it is probably nothing serious.
If the child experiences severe pain that limits his normal functions, it is necessary to rush to the emergency room immediately. In some cases, children with appendicitis complain of discomfort in the right leg due to the reflected pain.
Warning signs
In addition to stomach pain, you need to watch out for other signs. These symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain. Abdominal cramps are accompanied by vomiting with blood. Stool may also contain traces of blood.
- Vomiting of green liquid. This fluid could be bile, a sign of torsion or obstruction of the stomach or intestines. In these cases, we are faced with a real health emergency.
- Abdominal distension. It can be caused by appendicitis, but also by some other type of pathology.
- Pain when pressure is applied to the abdomen. In particular, if you apply pressure and then release immediately. In general, this pain means that the peritoneal lining, the membrane that covers the abdominal cavity, is inflamed.
- Adoption of a fetal posture. It happens when the baby experiences abdominal pain and lies sideways with the legs flexed towards the abdomen.
- Difficulty in maintaining posture for walking. the child feels abdominal pain and walks doubled over.
Treatment of appendicitis
Treatments for appendicitis require surgical removal of the appendix. If the baby’s appendix has not burst, antibiotics will be given to reduce the infection and proceed with extraction. When, on the other hand, the appendix has ruptured, in addition to its removal, irrigation of the peritoneal cavity is also necessary.
Once the appendix bacteria have been dispersed, major surgery is done as part of the treatment. The goal is to make sure that the bacteria present do not spread to other regions of the abdomen and cause a more serious infection.
Children whose appendix has ruptured will have to have a longer hospital stay. It is important that they start receiving intravenous antibiotic therapy, because the risk of infection is particularly high.









